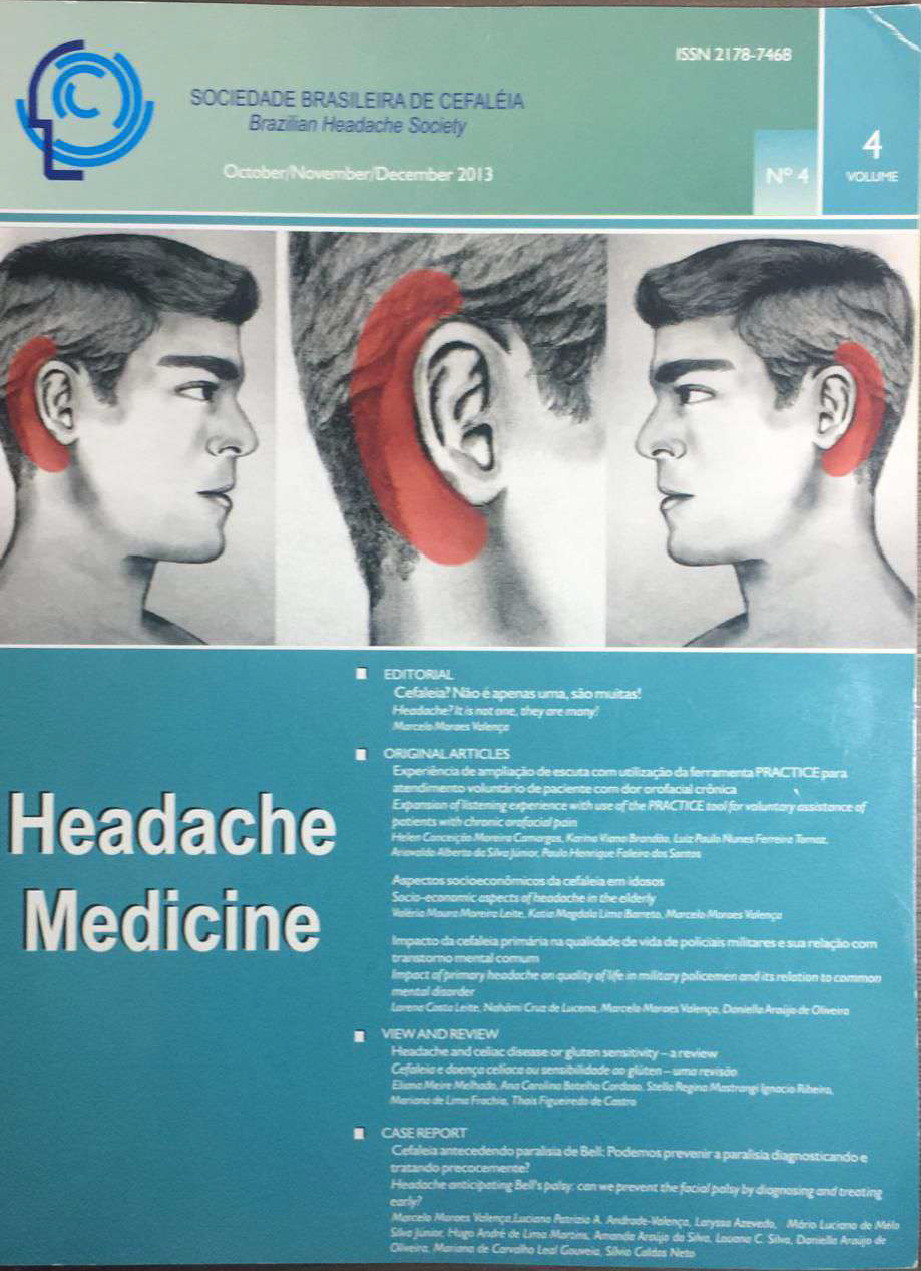
Headache anticipating Bell's palsy: can we prevent the facial palsy by diagnosing and treating early?
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.48208/HeadacheMed.2013.20Keywords:
Facial palsy, Diagnostic criteria, Diagnosis, HeadacheAbstract
Bell's palsy is a peripheral facial palsy with high incidence, which has some associated factors such as pregnancy, diabetes mellitus and hypertension, in addition to infection by some subtypes of the herpes virus, i.e. herpes simplex and herpes zoster sine herpete. A common feature of patients with Bell's palsy is the occurrence of ipsilateral headache of periauricular location, days before the onset of the paralysis. It is questionable, therefore, whether it is possible to identify a characteristic pattern of this pain in order to prevent disease progression or mitigate the possible development of motor deficit by initiating appropriate and immediate treatment to suppress the inflammatory process of the facial nerve. We report the case of a 50-year-old man with facial palsy on the right side, with pain in the ipsilateral retroauricular. At the age of 15 he reported a previous episode of facial palsy, also on the right side, with severe retroauricular pain, similar to the current recurrence. We propose diagnostic criteria for the retroauricular headache associated with idiopathic peripheral facial palsy.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2013 Headache Medicine

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.