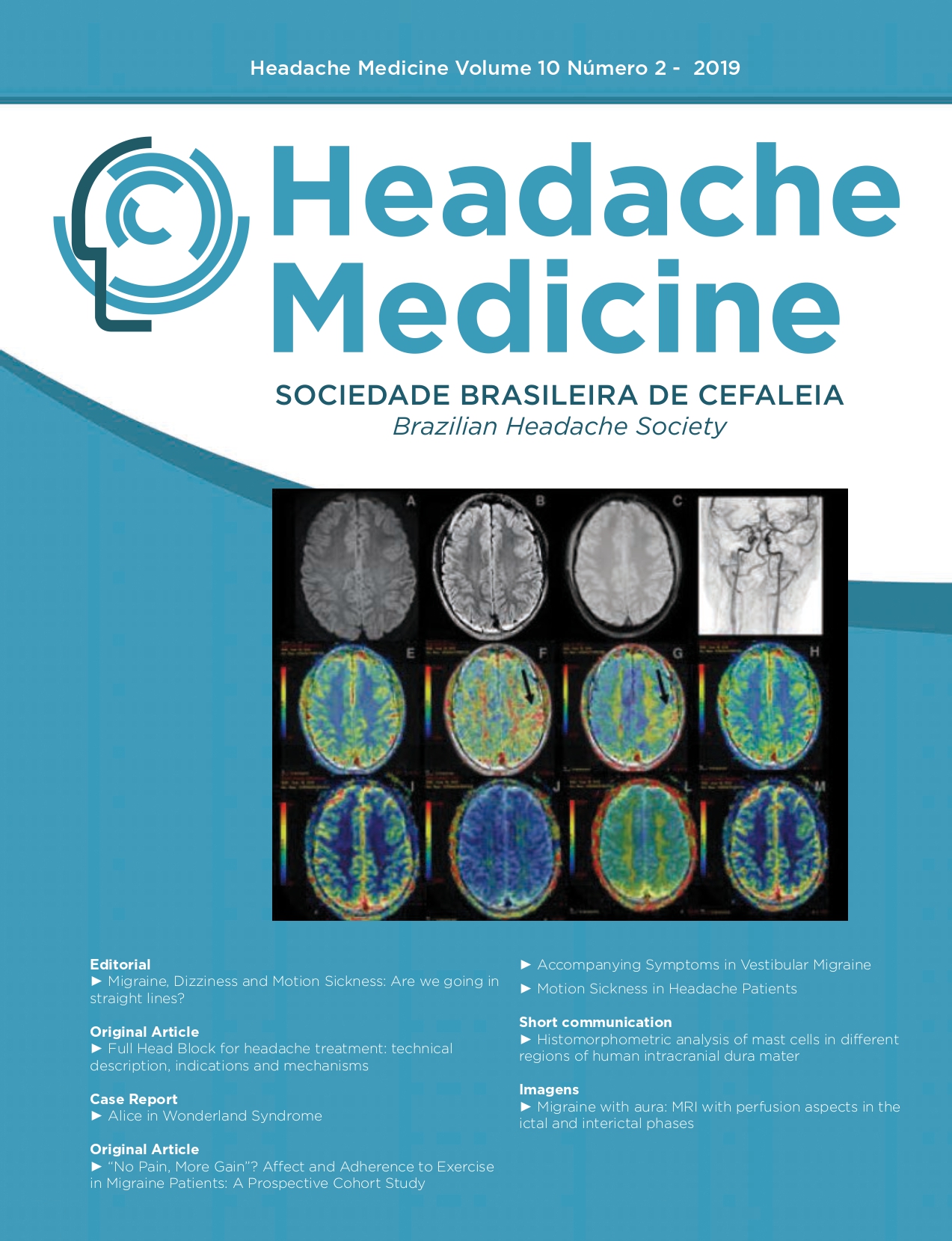
Accompanying Symptoms in Vestibular Migraine
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.48208/HeadacheMed.2019.14Keywords:
Migraine with aura, Migraine without aura, Vertigo, Vestibular disorders, DizzinessAbstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to classify the patients with vestibular migraine into the subgroups with and without aura, and to evaluate the occurrence of the accompanying symptoms of migraine in each subgroup. Methods: A prospective study performed at a tertiary center of vestibular migraine, with patients fulfilling definitive diagnostic criteria for vestibular migraine through International Classification of Headache Disorders ICHD-3 β. Patients were stratified in the subtypes with and without aura, and the accompanying symptoms were verified in each subgroup. Results: A total of 143 patients were included, 124 women and 19 men (86% and 13%, respectively). The mean age of onset of migraine in the patients ranged from 4 to 71 years (SD: 16.0) with a mean of 23 years, and an average headache frequency of 17 days per month (SD: 19.6), with a visual analog scale mean of 7.45 (SD: 1.88). Of the 143 patients evaluated, 101 (70%) had ICHD-3 β criteria for the diagnosis of migraine with aura. In patients with the migraine subgroup with aura, we found a higher relative risk for nausea 2,78 (CI: 0.15-1.0; p 0.04), vomiting, 2.65 (CI: 1.26-5.55; p 0.009), phonophobia 3,546 (1,647-7,637, p0,001), osmophobia 3,016 (1,219-7,462, p 0,014), kinesiophobia, 2,391 (1,128-5,071, p, 021), tinnitus 2,275 (1,062-4,873, 032), aural fullness 3,934 (1,519 - 10,192, p0,003), motion sickness associated with dizziness 3,924 (1,415 - 10,881, p0,006). Conclusion: In our center, migraine with aura was the most frequent subtype of migraine in patients with vestibular migraine. During the head attacks, some associated symptoms were more likely to occur in the aura subgroup, among them: nausea, vomiting, phonophobia, osmophobia, kinesiophobia, tinnitus, aural fullness and motion sickness accompanied by dizziness. In our sample, vestibular migraine associated with migraine with aura showed a higher risk of associated symptoms, suggesting that this subgroup is more severe, and with a more disabling disease.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2019 Headache Medicine

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.